NCITA, in partnership with the XNAT Team, the Institute of Cancer Research, and the Health and Bioscience IDEAS (Imaging, Data structures, gEnetics and Analytical Strategies) programme at University College London, hosted a highly successful 2021 XNAT virtual workshop on the 13-14th September 2021, with over 270 registered attendees.
The 2021 XNAT online workshop welcomed participants from across the globe to take part in a mixture of presentations, panel discussions, “town halls”, demonstrations and a poster session, with opportunities to collaborate and interact with each other throughout the event.
Day 1: PI focus
Starting with a warm introduction from Dr Daniel Marcus, Director of the XNAT Development Team, Day 1 focused on the high-level business impetus for XNAT and its future development. Dr Marcus highlighted the expansion of XNAT from neuroimaging into areas including cancer research – now a large focus of XNAT – as well as highlighting the roadmap for XNAT, including clinical integration, image interpretation, machine learning and preclinical imaging.
As part of the presentations, Dr Simon Doran, NCITA Repository Unit Manager, and Dr Ramona Woitek, University of Cambridge, presented case studies on ‘Using XNAT in Cancer Imaging Research’.
Case study: Using XNAT in Ovarian Cancer Imaging – Dr Ramona Woitek, University of Cambridge
Dr Ramona Woitek, Academic Radiologist at the University of Cambridge, presented a case study in ‘Using XNAT in Ovarian Cancer Imaging’. Dr Woitek outlined the challenges in High Grade Serious Ovarian Cancer (HGSOC), including the high mortality rates and low percentage of patients diagnosed at an early stage. The team have been exploring the extent to which they can predict patient response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), to guide when a patient should have surgery.
Through XNAT, Dr Woitek and her team created a multi-omics data set and looked to predict response using CT scans pre- and post-NACT through manual segmentation allowing volumetry and radiomics computation, combined with additional data sources including clinical data, CA-125, and ctDNA. Through the use of machine learning, the team found the integration of these data sources helped improve response prediction.
The team are now looking to validate their findings in a larger multicentric data set, harnessing data from fully anonymised CT scans from a multicentre trial to feed into the NCITA Repository. Dr Woitek highlighted the challenges and time intensity of manual segmentation and how the team are looking into the feasibility of automated segmentation through deep learning.
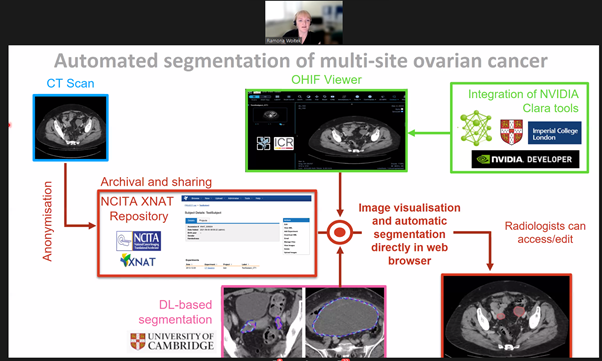
Dr Ramona Woitek, University of Cambridge, presents a case study in ‘Using XNAT in Ovarian Cancer Imaging’, at the XNAT 2021 virtual workshop
Dr Woitek also highlighted in her talk how imaging is a non-invasive way of monitoring and measuring heterogeneity. HGSOC is highly heterogenous and spreads easily throughout the abdomen, making it difficult to collect samples from different tumour deposits and challenging to monitor over time, therefore imaging is a highly suitable method for monitoring HGSOC. Dr Woitek’s work shows great potential in this area, and the team hope to facilitate precision medicine, leading to future prediction and personalised treatment for each patient.
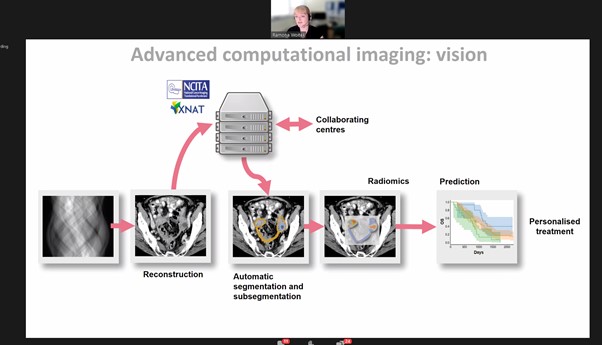
Dr Ramona Woitek, University of Cambridge, presents a case study in ‘Using XNAT in Ovarian Cancer Imaging’, at the XNAT 2021 virtual workshop
Case Study: Data Challenges for AI in Cancer Research – Dr Simon Doran, NCITA Repository Unit Manager
A second case study of using XNAT in cancer imaging research was presented by Dr Simon Doran, NCITA Repository Unit Manager, based at the Institute of Cancer Research.
In his talk, Dr Doran covered the aims and objectives of NCITA, highlighting how units across the UK work together to deliver advanced imaging studies. The NCITA Repository Unit provides an image repository and data management service for secure storage of imaging biomarker trial data and sharing of anonymised datasets between trials sites in multicentre clinical trials, and the unit uses XNAT to facilitate multi-centre trials.
Dr Doran discussed the advantages of using XNAT as a hub to store data from multi-centre trials, with the ability to process data in a variety of ways, including automatic segmentation and AI-based modelling, with the aim to store analysis in XNAT that can be audited and reproduced, including input and collaboration from researchers and clinicians across the globe.
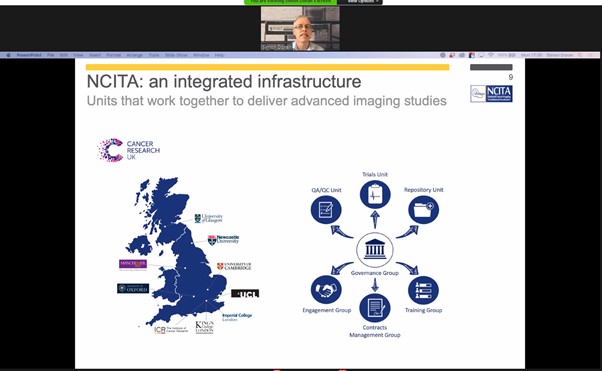
Dr Simon Doran, NCITA Repository Unit Manager, presents a case study in ‘Data Challenges for AI in Cancer Research’, at the XNAT 2021 virtual workshop
In addition, Dr Doran provided an overview of the data challenges in cancer imaging research, including the different requirements for algorithm development between three areas of cancer imaging research – experimental research, clinical trials, and routine healthcare data – and explained how XNAT could help with these challenges. Dr Doran also highlighted how the access tiers and data flow of research in XNAT can improve management of the flow of information in research, especially as data can be accessed from different locations. The vision of the team is to ensure easy access to all hierarchical levels of data, from the final results of a set of trials, back to an individual image voxel, as each level can provide a range of different insights.
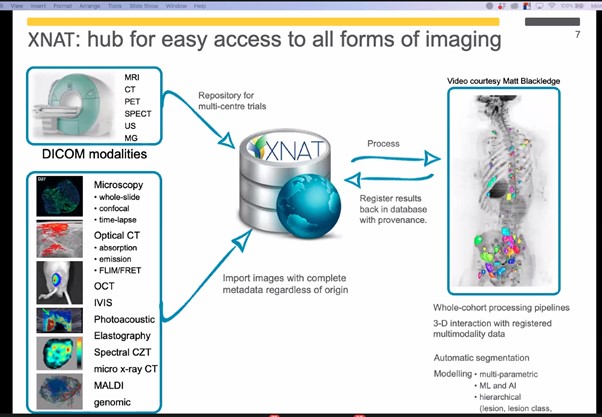
Dr Simon Doran, NCITA Repository Unit Manager, presents a case study in ‘Data Challenges for AI in Cancer Research’, at the XNAT 2021 virtual workshop
In a summary of key feature of XNAT for researchers, Dr Doran highlighted how XNAT can organise data according to project; data and metadata can be retrieved from anywhere in the world; arbitrary data can be stored in XNAT; there is extensible functionality with the use of plugins and container services; and XNAT is also open source.
Day 2 – Technical focus
The second day was focused towards experienced XNAT developers and administrators, providing an opportunity to dive deeper into the details of working with XNAT. In addition to talks and town hall discussions, XNAT hosted an interaction virtual poster session using the platform Spatial Chat, providing participants with the opportunity to attend interactive discussions.
Federated XNATs in NCITA – Dr Chris Rookyard, NCITA Repository Research Associate
Dr Chris Rookyard, NCITA Repository Research Associate, presented a poster on ‘Federated XNATs in NCITA’. His poster focused on how the NCITA Repository Unit is developing a federated XNAT framework in which data can be curated within institutions (which retain their own XNAT administrators and security procedures) but will allow data to be shared and cohorts to be built across institutions in a way that is individualised for each user.
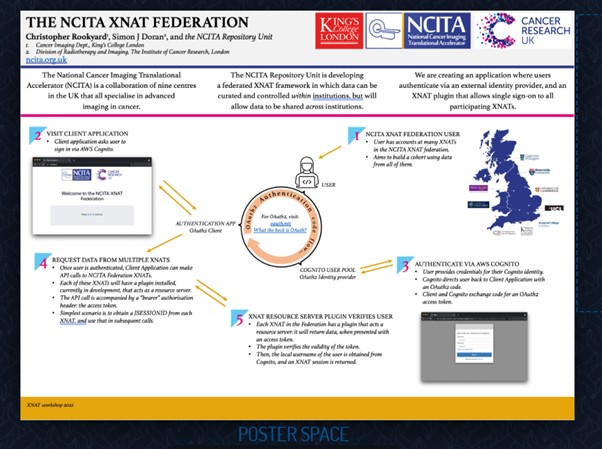
Dr Chris Rookyard presents a poster at the 2021 XNAT workshop: ‘The NCITA XNAT Federation’
For further information the workshop, including access to all recordings and poster submissions, click here: https://wiki.xnat.org/workshop-2021/


